Programs for making 3D printing models
The Best Programs for Making 3D Print Models
3D printing offers limitless possibilities, but to bring your ideas to life, you need the right modeling software. Whether you're designing precise mechanical parts, sculpting organic shapes, or creating digital copies of real-world objects, the right software will make all the difference. In this guide, we'll explore some of the best programs to create 3D models for printing, based on your specific needs.
Choosing the Right Program for Your Needs
The best 3D modeling software depends on what you want to create. Here are the main categories:
Accurate Objects – Ideal for functional parts, tools, or dimensioned objects. These models often require precision and parametric design tools to ensure measurements are exact and reproducible.
Organic Shapes – Best for soft, fluid forms like characters, animals, and terrain. Sculpting tools allow more flexibility in shape creation and artistic freedom.
Inorganic Shapes – Perfect for rigid, hard-edged structures like vehicles, robots, or buildings. These models require tools that support hard surface modeling techniques.
Real-World Copies – Used for scanning physical objects and turning them into 3D models. Photogrammetry and scanning software are essential for capturing real-world accuracy.
Each of these categories has specific tools best suited for the job. Let's break them down:
1. Parametric Design (For Functional & Accurate Models)
If your goal is to create models with precise measurements, calculations, and engineering designs, parametric modeling is the way to go. These programs allow for structured modeling, ensuring accuracy and easy adjustments.
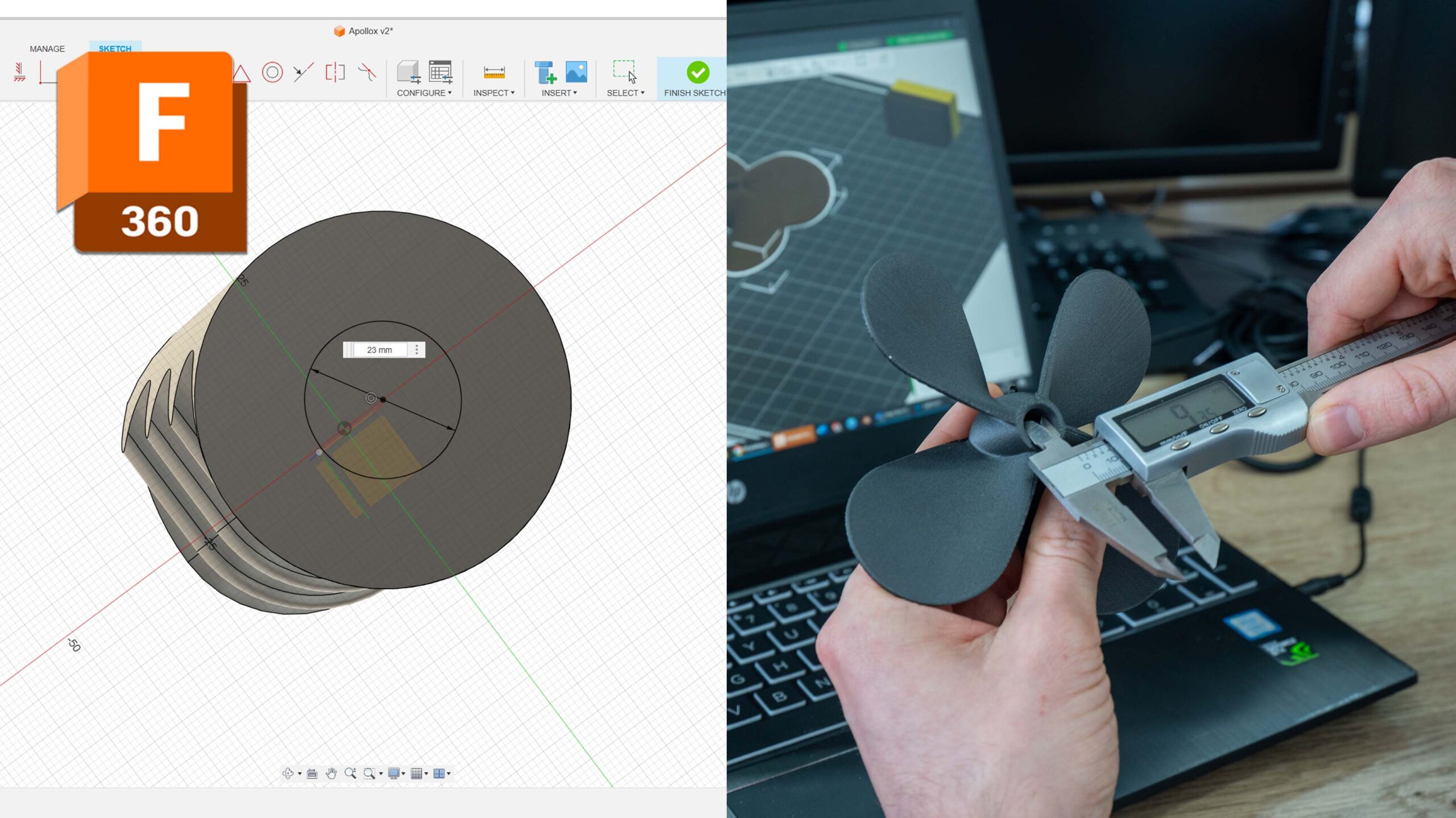
Fusion 360 – A powerful, cloud-based CAD tool developed by Autodesk. It offers parametric modeling, simulation tools, and assembly features, making it perfect for engineering and mechanical designs. It also has a free version for hobbyists and students.
OpenSCAD – A text-based, open-source modeling tool ideal for those comfortable with programming. Instead of using a graphical interface, users define models through scripting, making it great for repeatable and parametric designs. It is particularly popular in the maker community for creating precise, mathematical models.
Source: Autodesk Fusion360
2. Sculpting (For Organic Shapes & Characters)
Sculpting software mimics working with digital clay, allowing you to push, pull, and shape intricate details. This method is widely used for artistic modeling, character design, and organic structures.
SculptGL – A lightweight, browser-based sculpting tool that is great for beginners. It provides an easy introduction to digital sculpting without requiring downloads or installations. It has basic brushes and smoothing tools to shape models quickly.
ZBrush – The industry standard for digital sculpting. Used in game development, animation, and high-end 3D printing projects, ZBrush offers advanced brushes, dynamic tessellation, and high-detail capabilities. While it comes with a learning curve, it is unmatched in creating intricate, lifelike details.
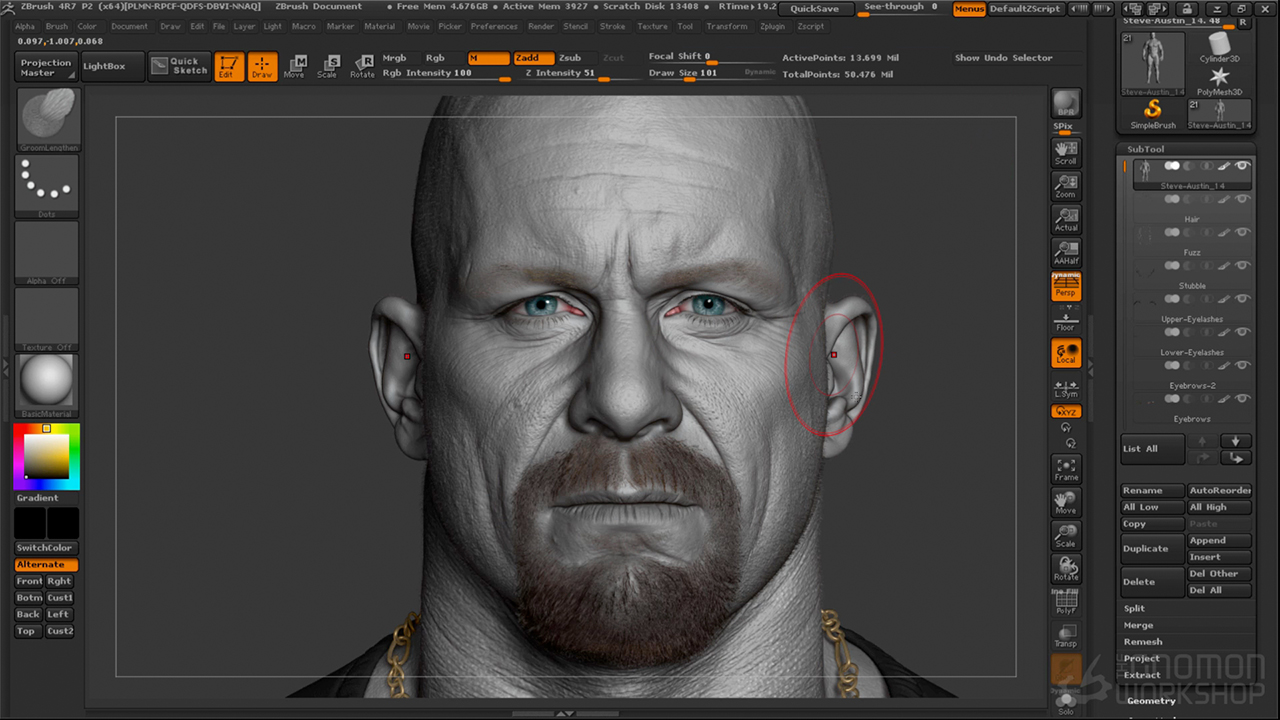
Source: The Gnommon Workshop
3. Hard Surface Modeling (For Mechanical & Inorganic Objects)
This type of modeling involves adding and subtracting geometric shapes to create complex forms. It is ideal for designing hard-edged objects like machinery, vehicles, and architectural models.
TinkerCAD – A simple and intuitive tool from Autodesk, perfect for beginners and children. It allows users to create models by combining basic geometric shapes. While limited in advanced features, it is an excellent starting point for understanding 3D design fundamentals.
Blender – A powerful, open-source tool that provides comprehensive 3D modeling features, including hard surface modeling. It has advanced modifiers, boolean operations, and a flexible workflow for precision modeling. Though it has a steep learning curve, it is an excellent option for those looking to refine their skills beyond beginner tools.
Source: Design & Technology Association
. Photogrammetry & Scanning (For Real-World Copies)
Want to create 3D models from real-life objects? Photogrammetry and scanning software let you convert images and scans into detailed 3D models, preserving accurate dimensions and textures.
AliceVision – An open-source photogrammetry tool that converts multiple images into 3D models. It requires minimal equipment—just a camera and a computer—to reconstruct detailed models. It is a great free alternative for those wanting to experiment with scanning.
Laser Scanning – A high-end scanning solution that captures objects with extreme detail. Laser scanners provide much greater accuracy and resolution than photogrammetry but come with high upfront costs. These scanners are often used in industrial applications, heritage preservation, and high-precision engineering.
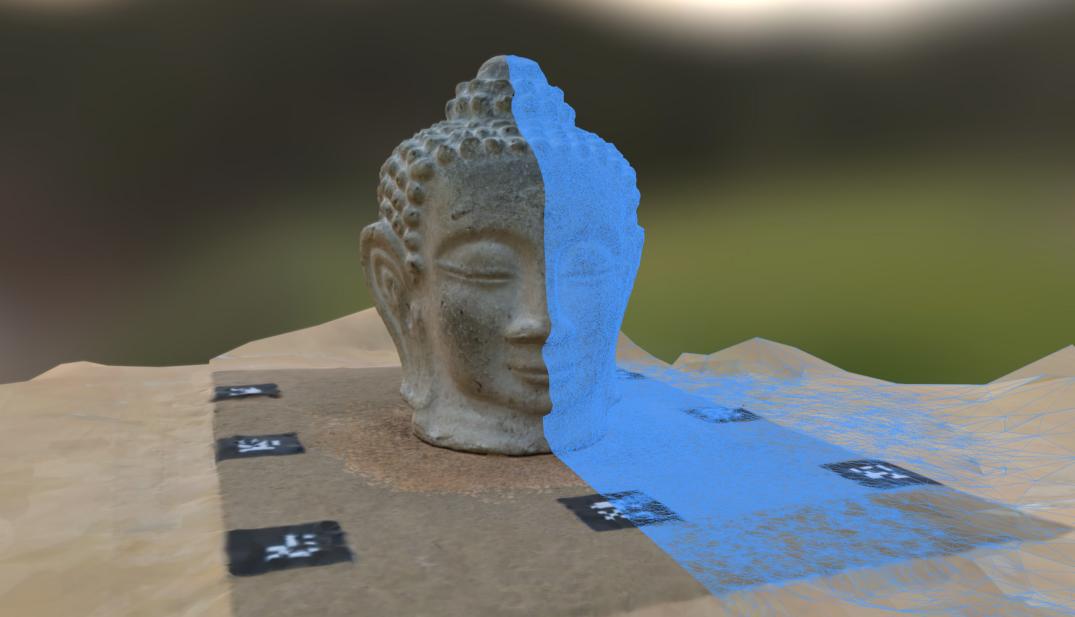

Source: AliceVision
Final Thoughts
No matter what you're creating, the right software will help bring your ideas to life. Whether you're an engineer designing precise components, an artist sculpting characters, or a hobbyist experimenting with scanning, there's a tool out there for you.
