Introduction
Are you starting your 3D printing journey? Choosing the perfect filament or resin is the key to turning your projects into masterpieces! With a plethora of options available, we're thrilled to share some game-changing tips and tricks with you.
By the end of this 3D printing guide, you'll be armed with all the knowledge about two of the best 3D printing materials out there: PLA vs PETG. Get ready with this guide for a deep dive into their characteristics, printing properties, techniques, subtypes, and how to pick the best one for your unique project!
Meet the Stars of the Show
PLA (Polylactic Acid) and PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)! These materials bring their own flair to the 3D printing scene, loved by both beginners and experts alike for their ease of use.
Picture your creations coming to life with these versatile filaments, turning your ideas into reality!
While PLA and PETG may seem similar at first glance, their differences are nothing short of fascinating! What are they used for, you ask? How do they stand apart? And most importantly, when should you choose one over the other? We've done the legwork, carefully examining PLA and PETG to help you uncover answers to these burning questions and more!
Hold tight as we unravel the magic behind these materials, offering insights that will elevate your 3D printing game. Are you ready to unleash your creativity and dive into the extraordinary world of PLA and PETG? Let the 3D printing adventure begin!
This guide introduces beginners to the world of 3D printing, focusing on the choice between PLA and PETG filaments. PLA, derived from natural sources, is eco-friendly and biodegradable. PETG, born from PET with glycol infusion, offers enhanced strength and durability, making it 100% recyclable. Both filaments are versatile but differ in characteristics, applications, and printing requirements.
PLA provides a smooth, glossy finish suitable for prototypes, while PETG offers superior strength and flexibility, making it ideal for functional parts. Printing with PLA is user-friendly due to lower temperatures, while PETG requires higher temperatures and a heated bed. Both share concerns about clogging printer heads.
Post-processing involves sanding, painting, and smoothing. PLA is generally easier to post-process due to its lower melting point. Applications vary; PLA suits prototypes and artistic creations, while PETG is preferred for durable, functional parts exposed to demanding conditions. PLA is more cost-effective, but PETG's enhanced properties contribute to a slightly higher price.
Recommendations depend on specific needs. If eco-friendliness and lower cost matter, choose PLA; for strength and durability, opt for PETG. The guide concludes that there's no one-size-fits-all answer in the PLA vs PETG debate. Users should experiment with both to understand their unique characteristics and make informed decisions based on their 3D printing needs.
Characteristics of PLA vs PETG
One of the primary distinctions between PLA vs PETG is, of course, how the two materials are manufactured.
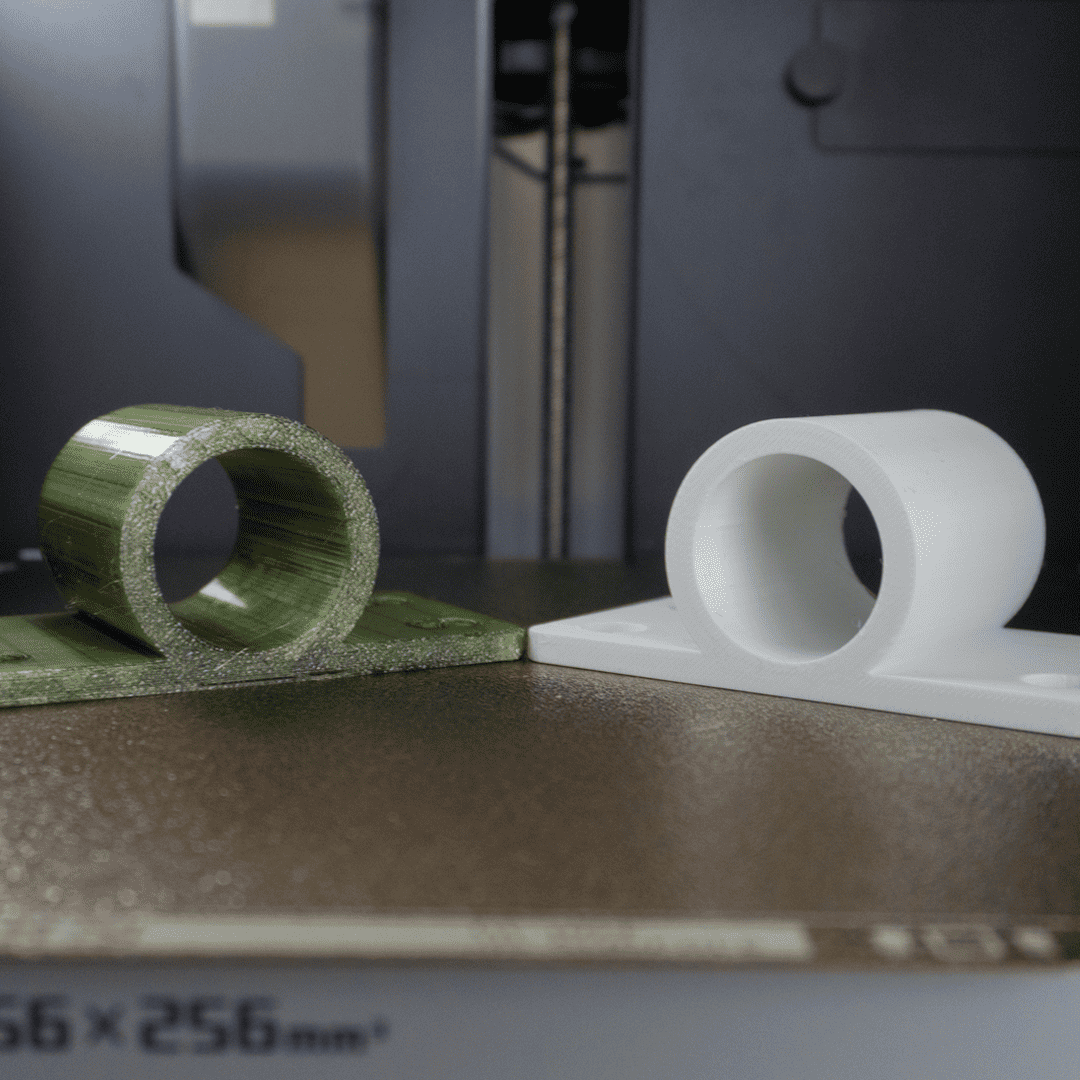
PLA - Nature's 3D Printing Wonder
First up, meet PLA, the champion of 3D printing! Sourced from renewable and natural raw ingredients like corn, cassava, sugarcane or beet pulp! PLA sets itself apart with its eco-friendly badge. PLA goes the extra mile by being biodegradable under specific conditions.
PETG - The Thermoplastic Powerhouse
Born from the thermoplastic giant PET, what makes PETG stand out? It's the infusion of glycol (G) at the molecular level, elevating its strength and durability compared to plain PET. While PETG proudly claims its spot as a 100% recyclable material, it's important to note that it stems from an oil-based polymer.
Properties
PLA - Aesthetic Elegance in Every Layer Seeking a visual masterpiece for your prototypes or display items? Look no further than PLA, the maestro of a smooth and glossy finish that captivates the eye. Marvel at its polished appearance, perfect for projects where aesthetics take centre stage. However, tread carefully if functionality is your muse, as PLA, with its lower heat resistance and brittleness, may not dance to the tune of robust functionality.
PLA
Easy to print
Brittle
Affordable
Low resistance to higher temperatures
Great for prototpying
Sensitive to moisture
PETG - The Versatile Virtuoso Enter PETG, the versatile virtuoso of the 3D printing stage! Striking the perfect chord between strength and flexibility, PETG emerges as a dynamic alternative to PLA. Picture this: resilience against water, chemicals, and fatigue, making PETG the go-to option for durability without compromising flexibility. It's the love child of ABS and PLA, showcasing superior strength (without reaching ABS extremes) and enhanced flexibility (without sacrificing too much like PLA). PETG steals the spotlight, addressing the shortcomings of both its filament predecessors.
Notably stiffer than PLA, PETG claims its territory, especially in the industrial arena. But that's not all—PETG can flex its muscles even more with carbon fibre reinforcement, elevating its strength while donning a premium price tag. While PLA can also dabble in carbon fibre reinforcements, PETG takes the crown, showcasing its inherent strength rooted in polymer dynamics. PETG stands tall in crafting components that dance between flexibility and shock resistance, creating a symphony of possibilities.
PETG
Strong and durable
Less colors and blends available
Higher UV resistance
Prone to warping and cracking
Resistant to heat and chemicals
Difficult to post process
Facing the elements
When it comes to facing the elements, PETG and PLA stand side by side, both lacking a UV protection halo. Yet, when we are looking at the question of PLA vs PETG, PETG shines a bit brighter against the onslaught of heat and UV exposure, standing resilient for extended periods. Safety takes centre stage with PETG and PLA, outclassing potential health hazards posed by ABS. While non-poisonous, a prudent approach is advised, considering the uncertainty surrounding the emission of fumes from any material.
How to print PLA vs PETG
Printing with PLA is favoured for its low printing temperature, typically ranging from 200-220°C. This makes PLA a user-friendly choice, as it adheres well to various bed surfaces, eliminating the necessity for a heated bed. Thanks to its low thermal expansion, warping issues are minimized, making PLA an excellent option for beginners. On the contrary, PETG demands a higher printing temperature, typically falling between 220-250°C. To prevent warping, a heated bed is recommended for PETG, and users should be mindful of ventilation, as PETG emits fumes during the printing process.
User friendly printing
Digging deeper into technical aspects, both PLA and PETG share notable similarities. Both are renowned for their user-friendly printing characteristics. PLA stands out as one of the simplest materials for 3D printing, making it a go-to for beginners. This simplicity is largely attributed to its lower printing temperatures, not requiring a heated bed or a closed chamber. PLA's optimal extrusion temperature ranges between 190-220°C, notably lower than PETG.
PETG, while considered user-friendly, falls slightly behind PLA in terms of ease. It doesn't demand a closed chamber, contributing to its straightforward printing process. However, due to the higher temperature requirements, PETG necessitates a heated printing bed, potentially limiting printer options for some users. Printing with PETG typically requires higher temperatures, ranging from 220-260°C, with the heating bed temperature ideally set between 75 and 90°C. It's worth noting that starting to print with PETG may pose initial challenges, unlike the smooth initiation with PLA. Yet, with proper settings, PETG is recognized for its easy extrusion and high thermal stability.
Both materials share a common concern regarding clogging printer heads due to their high viscosity. However, it's crucial to recognize that this challenge is not unique to PLA vs PETG, as many polymers face similar issues. Users shouldn't see it as a negative reflection on either material.
PLA General Printing Guidelines
Nozzle size: ≥ 0.1mm
Layer height: ≥ 0.05mm
Enclosure needed: No
Print temp: ± 200 – 220° C
Fan speed: 50-100%
Experience level: Beginner
Heat bed: ± 50 – 60° C
Adhesive: EasyFil Nr. I
PETG General Printing Guidelines
Nozzle size: ≥ 0.15mm
Layer height: ≥ 0.05mm
Enclosure needed: No
Print temp: ± 230 – 245° C
Fan speed: 10-25%
Experience level: Beginner
Heat bed: ± 80 – 90° C
Adhesive: EasyFil Nr. I
Post Processing
Post-processing is an essential aspect of 3D printing, and both PLA vs PETG can be sanded, painted, or smoothed with various techniques. However, PLA is generally easier to post-process due to its lower melting point. PETG, being more heat-resistant, requires careful handling during sanding and smoothing to avoid overheating and deformation.
One significant distinction between PETG and PLA is that post-processing is easier. PLA offers a greater range of post-processing options and is often easier to implement. Support structures, on the other hand, might be difficult to remove from PETG due to the material's adhesive qualities. To be successful, support structures must be spaced apart from the real model by at least 0.5mm; else, the printed part's structure may be damaged.

Sanding
Sanding, on the other hand, is an effective post-processing technique for both used to smooth the surface of an item, making it an extremely useful tool for people working with FDM procedures (which are utilized for both PETG and PLA filaments). This Technique is considered to be significantly easier with PETG, making it handy for anyone looking for a glossy finish (which PETG is also known for), but it is not difficult to perform with PLA. Plus, PLA offers more alternatives.
Another issue, particularly for those wishing to use printed parts as decoration or props, is that it's easy to paint PLA, but PETG doesn't allow for easy painting. PETG is noted for its ability to be transparent, which has its own benefits.
Resins
Finally, we want to mention the option of smoothing 3D prints with epoxy resins. Resins are a commonly used product that is made specifically for smoothing and finishing 3D printed models. It works generally by mixing two liquids and applying it evenly. After the curing time has passed, the model will have a glossy, smooth finish.
This method not only addresses imperfections but also brings out the intricate details of the printed object. It serves as a transformative step, taking a 3D print to a whole new level of professional-looking quality. The use of epoxy resins, opens up possibilities for achieving finishes that meet the highest aesthetic standards in the world of 3D printing.
Applications
The choice between PLA and PETG often depends on the intended application. PLA is excellent for simple prototype iterations, artistic creations, and objects that don't require high durability. PETG, on the other hand, is suitable for functional parts, mechanical components, and objects exposed to more demanding conditions. Its higher durability and resistance to heat and chemicals make it a preferred option for more durable prototypes, and engineering applications.
PLA and PETG applications overlap significantly. They are both employed in the food, medicinal, costume/prop production, and decorative components industries, but each material demonstrates its excellence in unique ways. For example, while considering PETG, the first application that comes to mind is the food business.
PET(G) is a substance used to produce water-resistant and durable containers, such as plastic bottles. Not to mention, PET(G) accounts for 18% of global plastic manufacturing, indicating that it is safe for contact with food. PETG has similar qualities, and it is FDA-approved.

The enhanced water resistance and superior heat resilience render qualities of PETG makes it an excellent choice for manufacturing various items. This characteristic makes PETG particularly well-suited for applications where exposure to water or elevated temperatures is a concern. On the other hand, PLA is also considered food-safe, although to a slightly lesser degree than PETG. While PLA has found application in the food industry, its lower water resistance compared to PETG may limit its suitability for certain food-related uses.
In terms of aesthetics, PLA outperforms PETG. As previously stated, PLA can be painted far more readily than PETG. Because the support structures are easily removed, more complicated, detailed pieces can be produced, making it ideal for ornamental elements and cosplay props.
Furthermore, one particularly intriguing aspect of PLA is that it is frequently used to simulate different materials. It can be used to generate hybrid filaments by combining PLA with other materials.
Price
When it comes to cost, PLA is generally more affordable than PETG. The raw materials used in PLA production are readily available and cost-effective, contributing to its lower market price. PETG, with its enhanced properties and durability, tends to be slightly more expensive.
PLA is commonly assumed to be substantially cheaper than PETG, but this is not always the case.
PLA
PETG






EasyFil ePLA
EasyFil PLA
ReFill PLA
EasyFil ePETG
HDGlass
ReFill PETG
250g - 8000g
250g - 2300g
750g - 2000g
250g - 8000g
250g - 8000g
750g - 2000g
1.75mm & 2.85mm
1.75mm & 2.85mm
1.75mm
1.75mm & 2.85mm
1.75mm & 2.85mm
1.75mm
From €9,99
From €11,50
From €15,00
From €11,00
From €13,50
From €16,99
Something to keep in mind with both materials is that what causes the price to change is the quality of the filament; both materials can vary dramatically in quality, from low-grade filament intended for amateurs to semi-industrial materials. Also, any PLA or PETG filaments containing other components, like as carbon fiber, will be more expensive.
When looking for filament, compare PLA vs PETG based on your individual demands.
Recommendations
Ultimately, the choice between PLA and PETG depends on your specific requirements and the intended use of your 3D prints. If you prioritize eco-friendliness, ease of use, and lower cost, ReFill PLA or our ReForm rPLA may be the right choice for you.
On the other hand, if you need stronger, more durable prints with resistance to heat and chemicals, EasyFil PETG is worth considering.
It's often beneficial for users to experiment with PLA vs PETG to test these different types of filaments to understand their unique characteristics and determine which best suits their individual projects.
PLA
ReFill PLA
EasyFil ePLA
ReForm – rPLA
PLActive
MetalFil – Classic Copper
MetalFil – Ancient Bronze
EasyFil PLA – Glow in the Dark
Volcano PLA
Tough PLA
StoneFil
Premium PLA
Matt PLA
PETG
ReFill PETG
EasyFil ePETG
ReForm – rPET
Addigy F3040
High Precision PET
HDglass
EasyFil PET
CarbonFil
Conclusion
In the PLA vs PETG debate, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. Each filament has its strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different applications. By considering factors such as printing characteristics, properties, post-processing requirements, applications, and price, you can make an informed decision based on your specific 3D printing needs.
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, experimenting with both PLA and PETG will provide valuable insights into their capabilities and help you achieve successful 3D prints.






































