Material Guide – TPU Filament

If you 3D print with rubber-like flexibility & industrial strong filament, you might agree that it's hard to get it exactly right. To help you get started and learn how to print with FormFutura TPU, we wrote this Material Guide - TPU Filament!
By the end of this 3D Printing Material Guide, you'll be armed with all the knowledge about TPU characteristics, printing properties, techniques, subtypes, and how to pick the best one for your unique project!
The Stars of the Show
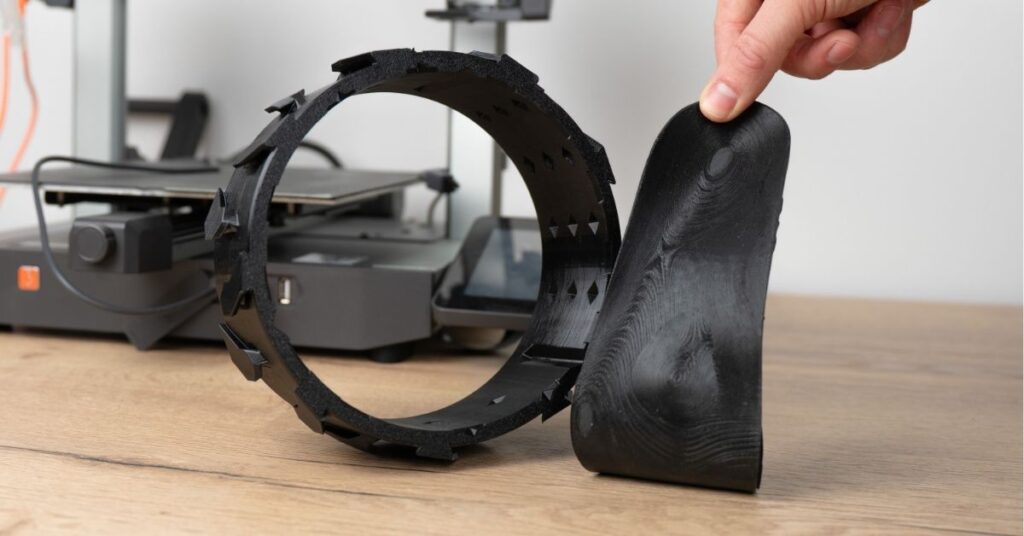
Python Flex is a very flexible type of 3D printer filament. This makes it the perfect filament for 3D prints that require to be strong and resilient while maintaining its flexibility and elasticity.
Python Flex 98A - Python Flex TPU 98A is a flexible type of 3D printer filament with a shore hardness of 98A, which falls on the firmer side of flexible filaments, similar to a bendy phone case but not as soft as a rubber band. This makes it perfect for 3D printing strong and resilient parts that require flexibility and elasticity.
Python Flex 90A - Python Flex TPU 90A is a very flexible type of 3D printer filament with a shore hardness of 90A. This indicates a softer and more elastic material compared to TPU 98A, resembling the flexibility of a thick rubber band. It's ideal for applications requiring high flexibility and stretch, such as gaskets, seals, and grippers.
Characteristics
High elasticity and flexibility: TPU is known for its ability to stretch up to 500% and bend without breaking, making it an ideal material for applications that require flexibility.
Excellent printability: TPU is relatively easy to print compared to other flexible filaments like TPE. It adheres well to the print bed and exhibits minimal warping during the cooling process.
Recommended printing settings: For optimal results, print TPU at a temperature between 220°C and 250°C and a speed of 20 to 30 mm/s.
Direct drive extruder recommended: To prevent the filament from bending or curling during printing, it's advisable to use a direct drive extruder that provides adequate support for TPU.
Chemical resistance: TPU is insoluble and resistant to oils, greases, and chemicals, making it suitable for applications that require durability in harsh environments.
Wide temperature range: TPU can withstand a broad range of temperatures, both low and high, making it versatile for various applications.
Pro's and Con's
![]() Recyclable
Recyclable
![]() High Elasticity and Flexibility
High Elasticity and Flexibility
![]() Excellent Abrasion Resistance
Excellent Abrasion Resistance
![]() Resistant to oil, grease and chemicals
Resistant to oil, grease and chemicals
![]() Heated bed is not required due to the excellent layer adhesion
Heated bed is not required due to the excellent layer adhesion
![]() Low Print speed
Low Print speed
![]() Less suitable for Bowden Extrusion
Less suitable for Bowden Extrusion
![]() Less suitable for Bridging parts
Less suitable for Bridging parts
![]() High print temperatures
High print temperatures
TPU Print Settings
Nozzle Size: ≥ 0.25mm
Bed Temperature: ± 50 – 60° C
Print speed: Slow - Fast
Nozzle Tempeature: ± 220 – 250° C
Filament Drying: Required*
First Layer Cooling: No
Layer Cooling: 20-50%
Enclosure: Optional
*Don't skip the drying step! TPU is prone to absorbing moisture from the air, which can lead to printing problems like bubbles and weak layers. To ensure successful prints, thoroughly dry your TPU filament for at least 24 hours at 50°C (122°F) before printing. You can even keep the filament drying while printing for optimal results.
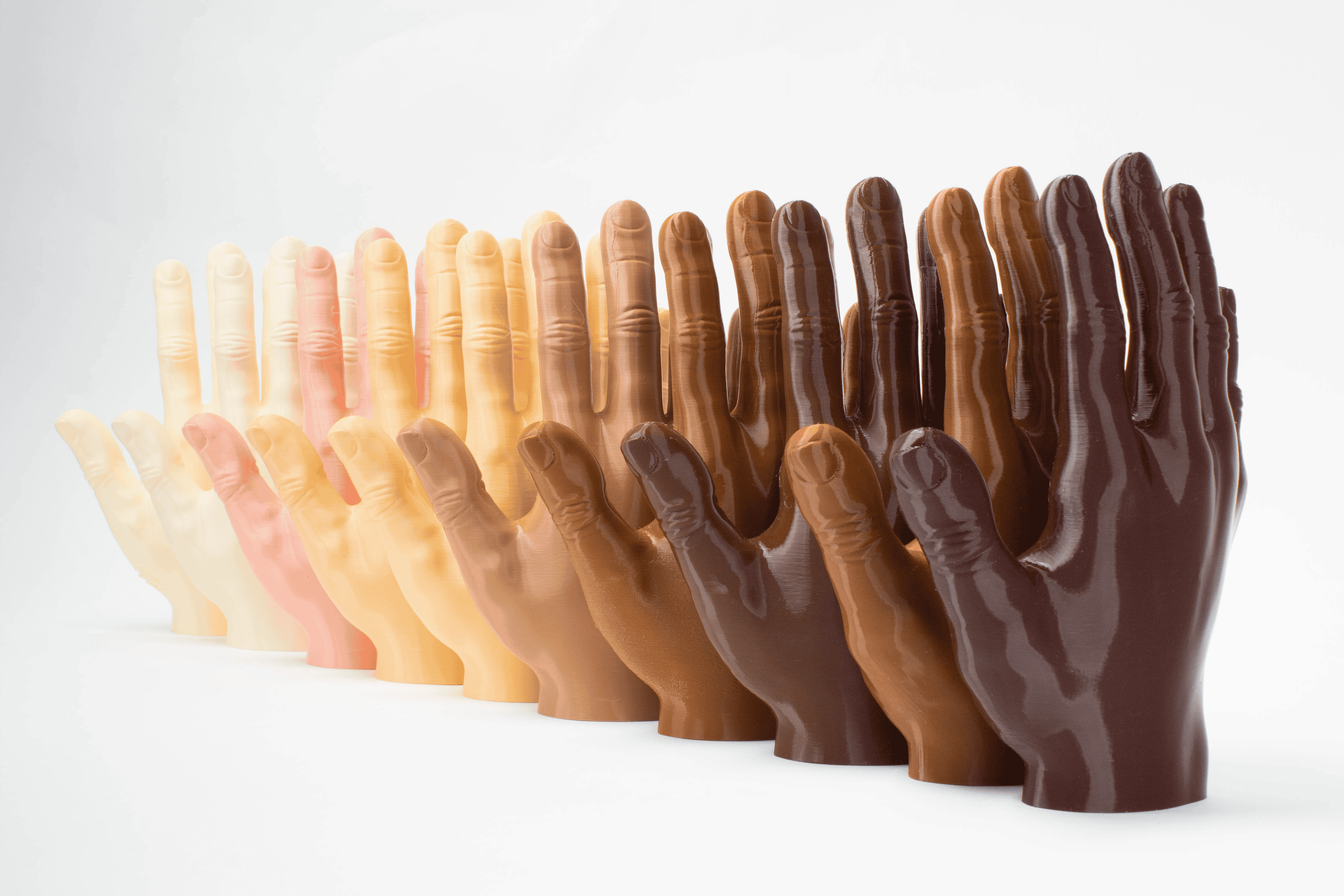

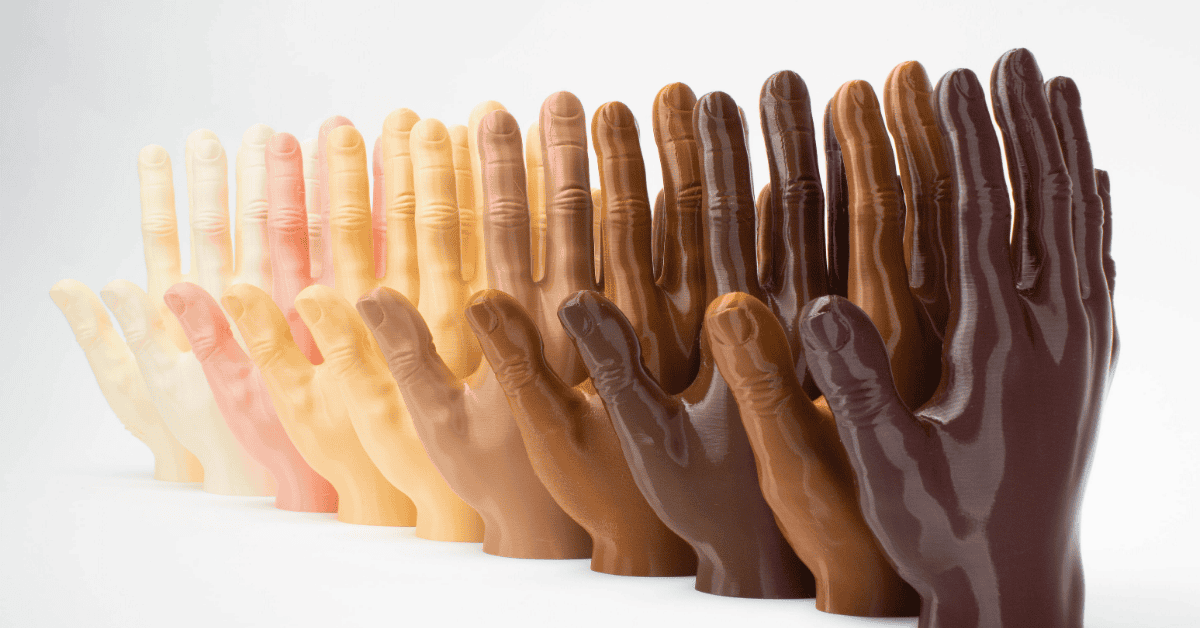
Tips for Printing TPU
Keep TPU filament dry: Store TPU filament in a dry place, preferably in a sealed bag with desiccant or silica gel, to prevent moisture absorption and air bubbles in your 3D prints.
Shore A scale: The hardness of TPU is measured on the Shore A scale, with higher values indicating a harder and less flexible material. Choose the appropriate TPU hardness for your specific application.
Heated bed: If printing without a heated bed, use painter’s tape or adhesive spray to ensure good first layer adhesion. Poor adhesion can lead to cracking when the object is flexed or stretched.
Direct drive extruder: For optimal TPU printing, use a direct drive extruder that provides adequate support for the filament, preventing it from bending or being pushed in the wrong direction.
If using a Bowden extruder: Ensure the filament does not get stuck against the Bowden tube wall.
Disable or limit retraction: Disable or minimize retraction to max ± 5mm for TPU printing, as excessive retraction can cause filament jams.
Printer settings: Adjust printer settings specifically for flexible filaments before printing with TPU. Use the settings from this blog and experiment what works best for your 3D printer!
Additional Tips:
Dry your TPU filament before printing: Moisture can cause printing problems, so drying your filament beforehand can improve print quality.
Use a textured print bed: A textured print bed can provide better adhesion for TPU, especially on the first layer.
Experiment with different print settings: Find the optimal print settings for your specific TPU filament and printer.
Be patient: TPU printing requires more patience and experimentation compared to other filaments.
By following these tips, you can achieve successful and high-quality TPU 3D prints. Remember to always refer to the specific recommendations for your chosen TPU filament and printer.